US EPA
Is radon really bad for you?
Breathing radon over time increases your risk of lung cancer. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Nationally, the EPA estimates that about 21,000 people die each year from radon-related lung cancer. Only smoking causes more lung cancer deaths.
You'll face very low boosted danger of establishing lung cancer cells due to radon if you can keep your indoor radon levels at 2 pCi/L or lower. Only two non-smokers out of 1,000 will certainly create lung cancer cells particularly due to the direct exposure when you reach the 1.3 pCi/L level that is normal for indoor air.
Persistent direct exposure to radon gas raises the danger of establishing lung cancer. In the USA, an estimated 21,000 individuals die from radon-related lung cancer cells annually (compared to 160,000 lung cancer fatalities from smoking cigarettes), according to the EPA. Radon is the 2nd leading cause of lung cancer, and it's the leading source of lung cancer cells in nonsmokers, according to the agency.
Is radon mitigation really necessary?
When radon gas enters the body, it exposes the lungs to small amounts of radiation. In small quantities, experts say this is harmless. However, in persistent exposures or larger quantities, radon can damage the cells of the lining of the lungs, increasing a person's chance of developing lung cancer.
The initial significant studies with radon and also wellness occurred in the context of uranium mining, first in the Joachimsthal region of Bohemia and after that in the Southwestern United States throughout the early Cold Battle. Underground uranium mines may have high focus of radon since radon is an item of the radioactive degeneration of uranium. Several uranium miners in the Four Corners region contracted lung cancer cells and also various other pathologies as a result of high degrees of exposure to radon in the mid-1950s. The findings were released in the journal Health Physics in 2008.
- Lung cancer danger climbs 16% per 2.7 pCi/L increase in radon exposure.
- Radon gas is a naturally-occurring by-product of the radioactive decay of Uranium in the soil.
- Depending on your geographical location, the radon levels of the air you take a breath outside of your home may be as high as 0.75 pCi/L.
- The nationwide average of outside radon levels is 0.4 pCi/L and it is estimated by the National Academy of Sciences that outdoor radon levels cause about 800 of the 21,000 radon caused lung cancer fatalities in the US each year.
- The United States EPA has put it plainly, stating, "Any type of radon exposure has some danger of triggering lung cancer cells.
How do you eliminate radon?
Possible symptoms include shortness of breath (difficulty breathing), a new or worsening cough, pain or tightness in the chest, hoarseness, or trouble swallowing. If you smoke and you know you've been exposed to high levels of radon, it's very important to quit smoking.
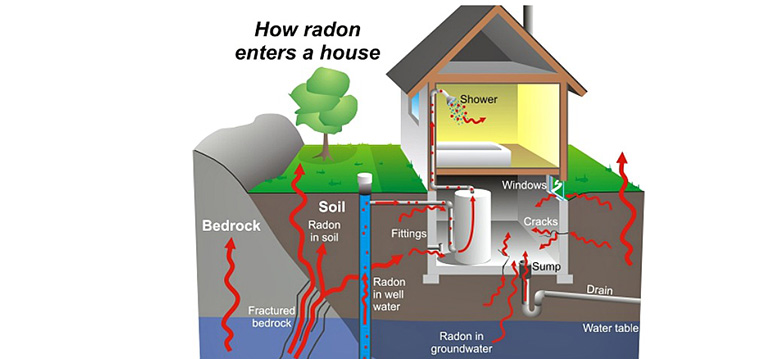
January is National Radon Activity month and also the Environmental Protection Agency is asking homeowners to "conserve a life" by testing for radon as well as taking care of any troubles they locate. Radon is a contaminated gas and exposure to it causes 21,000 lung cancer cells deaths each year-- just smoking cigarettes causes more. Because you can not see, scent or preference radon, it is necessary to occasionally examine the air in your house.
What are the symptoms of radon in your home?
If a person has been exposed to radon, 75 percent of the radon progeny in lungs will become "harmless" lead particles after 44 years. When an alpha particle damages a cell to make it cancerous, the onset of lung cancer takes a minimum of 5 years but most often 15 to 25 years, and even longer.

Radon-222 has been categorized by International Agency for Research on Cancer cells as being carcinogenic to humans. There is sufficient evidence for the carcinogenicity of radon and its decay items in human beings for such exposures. He was told that residing in the home was the equivalent of smoking 135 packs of cigarettes a day, as well as he and his family had boosted their risk of developing lung cancer by 13 or 14 percent.
How long does it take for radon to cause cancer?
Fact: You will reduce your risk of lung cancer when you reduce radon levels, even if you've lived with an elevated radon level for a long time. Keep in mind that radon levels below 4 pCi/L still pose radon1.com/who-pays-for-radon-mitigation-secrets/ some risk and that radon levels can be reduced to 2 pCi/L or below in most homes.